Unpacking the AI Lexicon: Words You Need to Know
As artificial intelligence (AI) continues its rapid evolution, it brings along a complex vocabulary that can bewilder both newcomers and seasoned tech enthusiasts alike. Just like the cryptocurrency boom birthed its own set of terms, the AI revolution has led to a linguistic shift that demands attention. In this piece, I will delve into 20 essential AI-related words and their meanings—helping you navigate this fascinating, yet daunting landscape.
Understanding AI: More Than Just a Buzzword
At its core, artificial intelligence refers to machines and systems designed to simulate human intelligence. The current discourse is heavily focused on these tools that can generate art, mimic conversation, or transcribe a spoken word. However, whether we should consider these tools as genuinely “intelligent” remains a topic of vigorous debate. Today’s AI landscape is dominated by applications transforming everything from content creation to data processing.
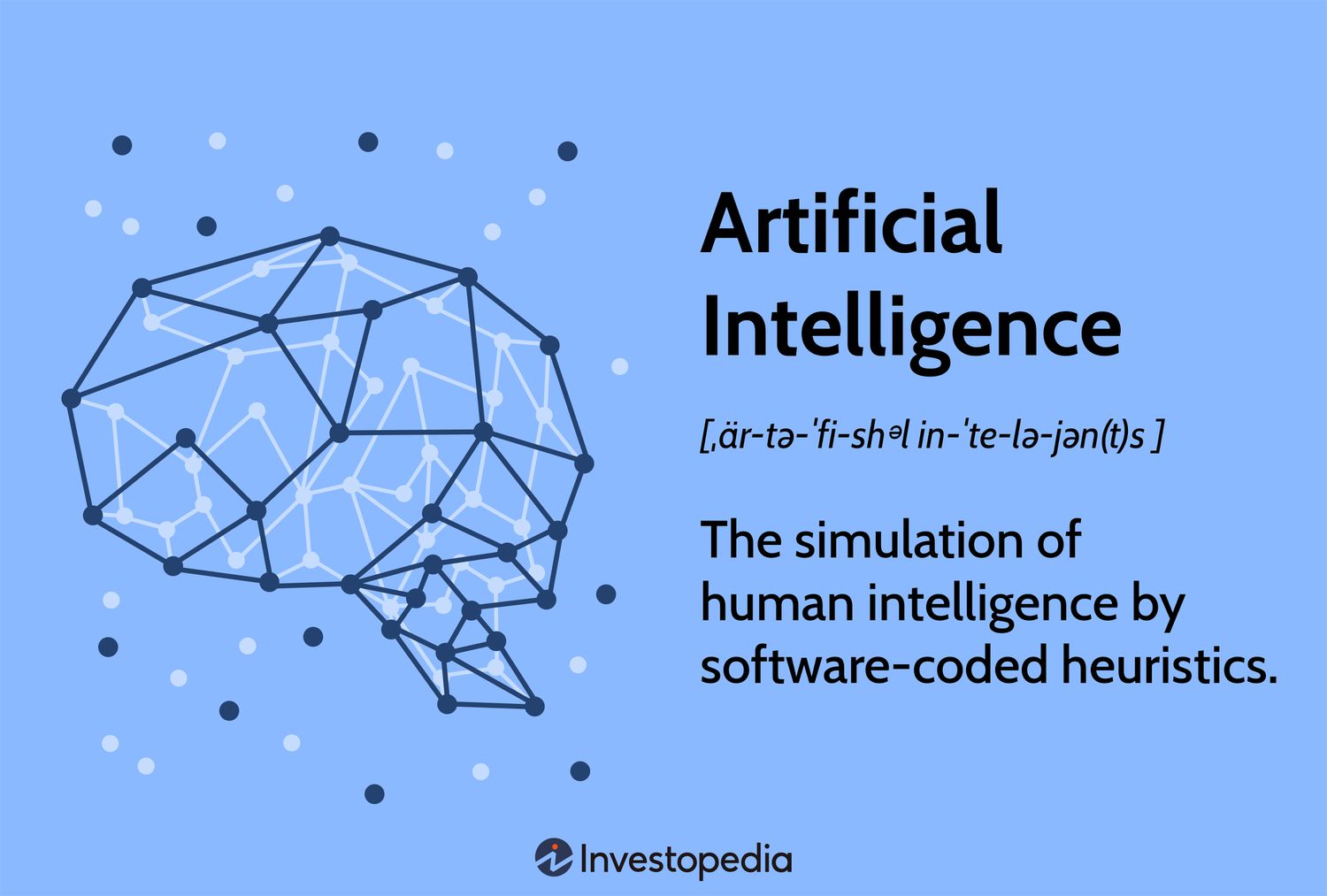 Visual representation of artificial intelligence development.
Visual representation of artificial intelligence development.
The Mechanics Behind AI: Algorithms and Bias
At the heart of AI are algorithms, which are sets of rules or instructions that guide computer programs. We see them at play in search engines or social media feeds, subtly shaping our internet experience. However, this power comes with responsibility. Bias is a significant issue in AI, stemming from flawed algorithms that may yield incorrect results. An all-too-common example is speech recognition tools failing to understand diverse English accents, underscoring the importance of diverse training data.
Conversational AI: The Rise of Digital Communication
The era of conversational AI has brought forth chatbots and voice assistants that we engage with daily. These user-friendly tools enhance our interactions with technology, making it easier to ask questions or carry out tasks. For anyone who has asked Siri for the weather or typed a query into a chatbot, you’re already part of this AI evolution.
Data Mining and Insights: Mining for Gold
Data mining is the process of sifting through vast amounts of information to uncover insights or trends. For example, businesses often lean on data mining to optimize sales strategies or enhance customer experiences. Knowing where to look for patterns can be the difference between success and failure in competitive industries.
Deep Learning: Mimicking the Brain
A pivotal facet of AI is deep learning, designed to emulate the human brain’s learning process using multiple layers of networks. While this technology powers advancements like self-driving cars, it’s the repetition in training with vast datasets that allows AI to recognize objects or actions, such as identifying stop signs with astonishing accuracy.
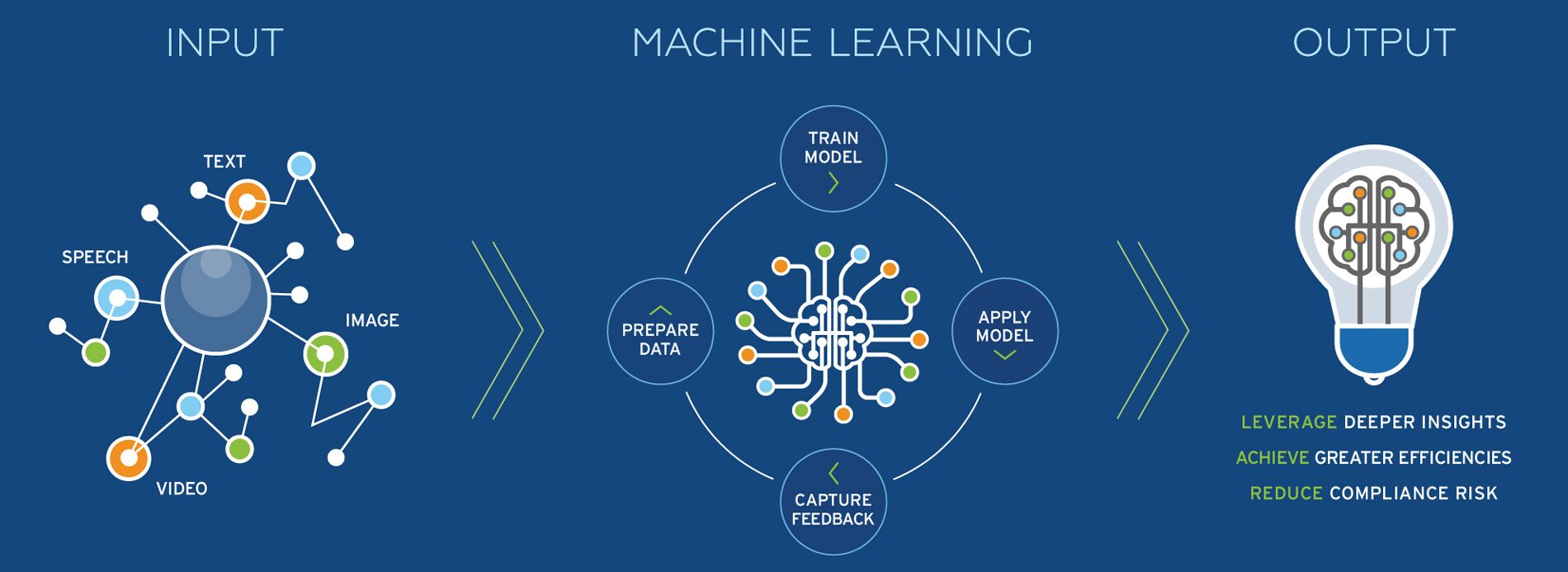 Understanding deep learning in AI systems.
Understanding deep learning in AI systems.
Large Language Models (LLMs): The New Text Generators
The advent of large language models (LLMs) has transformed our interactions with technology further. Designed to process and generate text, tools powered by LLMs, like OpenAI’s GPT-4, can comprehend and respond to queries in human-like ways. They are not just limited to generating text; they can also summarize vast content, making information more accessible than ever.
Generative AI: Creative Machines
Generative AI is another fascinating development, enabling machines to create art, images, or even written content from basic prompts. Whether crafting visual art or adopting different styles, these models turn abstract inputs into tangible outputs—thereby redefining creative boundaries between human and machine.
Hallucination: The Dark Side of AI Outputs
However, embracing AI comes with caveats. Hallucination reflects moments when AI confidently presents fictitious information as fact. This often stems from inaccuracies in the data it draws from, and understanding this phenomenon is crucial for anyone engaging with AI technologies. To quote a well-respected writer on the subject:
“Lifehacker writer Stephen Johnson has great advice for spotting AI hallucinations.”
Beyond Recognition: Image and Speech Interpretation
With applications like image recognition, AI can decipher specific subjects within photos—crucial for sectors like healthcare or wildlife conservation. Parallelly, speech recognition technology interprets human words, further bridging the gap between language and understanding for AI tools.
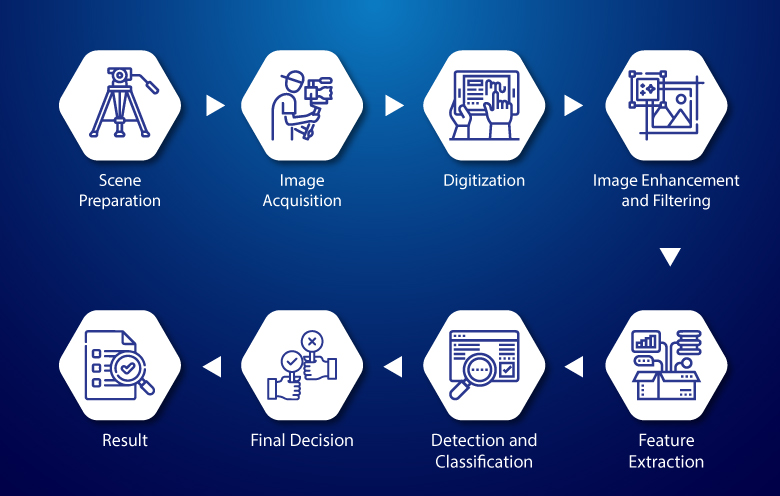 The capabilities of AI in visual interpretation.
The capabilities of AI in visual interpretation.
Machine Learning: AI’s Learning Backbone
A significant umbrella term, machine learning, refers to algorithms that enhance their functions through experience. Deep learning, as mentioned before, falls under this broader category. Each interaction teaches the algorithm something new, refining performance and honing capabilities over time—an ongoing learning journey inherent in the AI experience.
The Language of AI: Natural Language Processing
Natural language processing (NLP) is the field that enables machines to understand human language. It powers your smartphone’s calendar functionality and voice assistants’ insightful replies. NLP is the magic that makes our day-to-day interaction with machines feel seamless, turning casual dialogue into actionable insights.
Neural Networks: The Brain Behind AI
At the root of many deep learning innovations lies neural networks, which mimic our brain’s architecture, allowing for intricate data processing. This system is what enables machines to conduct complex tasks, from recognizing your face to generating compelling narratives.
The Technical Side: OCR and Prompt Engineering
Beyond recognition lies optical character recognition (OCR), which extracts written words from images. It opens doors to digitizing documents and enables quick searches through extensive texts. Furthermore, the expertise in prompt engineering is vital for deriving the best results from generative AI tools. Crafting precise prompts can unlock the true potential of these advanced systems, transforming user interaction into an art form of its own.
Reinforcement Learning: Teaching AI
AI continues to evolve, thanks in part to reinforcement learning from human feedback (RLHF). This iterative process trains AI by providing corrective feedback, enabling it to deliver more accurate results faster. Our input guides its learning, shaping the technology to better meet our needs.
Decoding AI: Tokens and Training Data
In practical terms, AI operations often rely on what are known as tokens—pieces of text that feed into the system. For instance, when utilizing a GPT model, pricing structures are based on token consumption. This focus on tokens goes hand in hand with training data, the foundation that algorithms use to learn and perfect their capabilities—often sourced from the most trafficked websites around the globe.
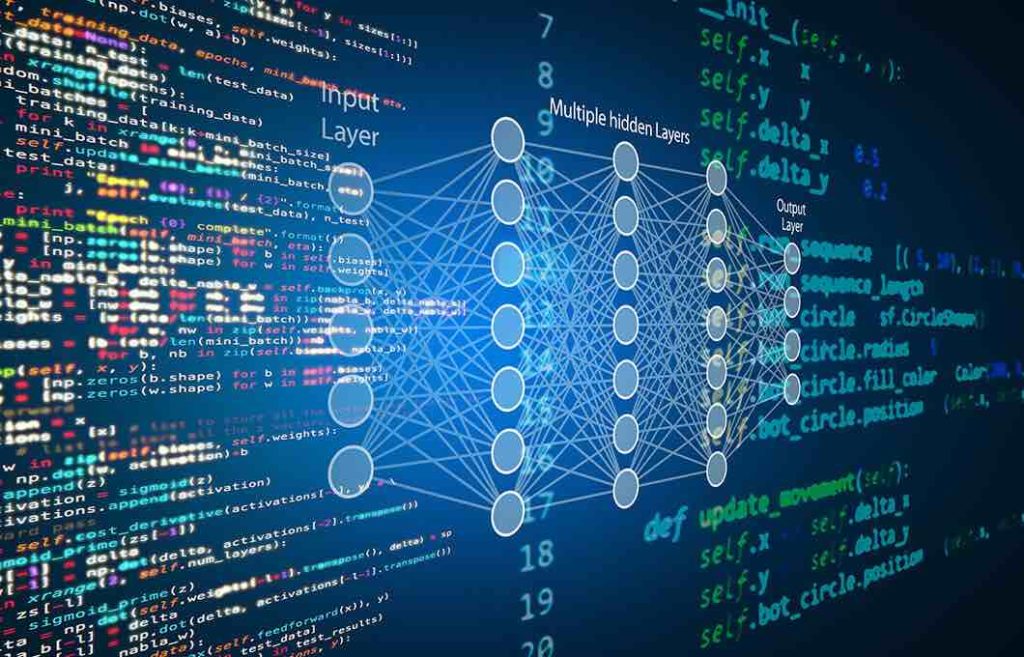 Understanding training data in machine learning.
Understanding training data in machine learning.
Philosophical Reflections: The Turing Test
Lastly, let’s not overlook the impact of the Turing Test, conceived by Alan Turing. It serves to measure a machine’s ability to exhibit human-like intelligence. If a computer can fool a human into believing it is also human, it has passed the Turing Test—a fascinating benchmark in AI development.
Conclusion
As we stand on the brink of unprecedented advancements in artificial intelligence, familiarizing ourselves with this new vocabulary is paramount. It is not merely about understanding what these words mean but also about grasping their implications for the future of technology and society. As our world becomes increasingly intertwined with AI, each term carries weight, shaping our understanding and expectations of the capabilities ahead. Being informed is not just advantageous; it’s essential in this brave new digital frontier.















