Federal Agencies Embrace Generative AI: Pioneering Applications and Ensuring Safeguards
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) within federal agencies is on the rise, particularly as generative AI technologies begin to gain traction. With various branches of the U.S. government exploring novel applications, the balance between innovation and responsibility remains crucial. This article examines how agencies like the U.S. Air Force, Government Accountability Office (GAO), and the Office of Personnel Management (OPM) are engaging with generative AI while ensuring it aligns with safeguards and ethical considerations.
The Air Force’s Innovative Leap into Generative AI
For years now, the U.S. Air Force has been at the forefront of technological advancements, utilizing AI analytics for everything from predictive maintenance on aircraft to the development of autonomous fighter jets. Following the emergence of generative AI, it comes as no surprise that the Air Force is pioneering its own innovations in this field. The branch has introduced a new application known as NIPRGPT, which was launched in June after a year of development.
NIPRGPT comprises two key functionalities. The first feature mimics ChatGPT, providing users with the ability to query and search for information sourced from the expansive datasets the model has been trained on. The second feature offers a more personalized experience via retrieval-augmented generation, where users can upload their own content, enabling them to ask specific questions related to their materials.
“We see use cases that can help us save time and increase productivity across the board.”
— Chandra Donelson, Acting Chief Data and AI Officer, U.S. Air Force
Currently, the application is available to a limited number of users with a gradual rollout planned for future expansion. Indeed, user training is built into the onboarding process, allowing personnel to experiment with various use cases, fostering a culture of exploration and innovation within the agency.
 A glimpse into the integration of AI within the U.S. Air Force.
A glimpse into the integration of AI within the U.S. Air Force.
GAO: Oversight Meets Innovation
At the Government Accountability Office, the approach to generative AI is distinctively dual-faceted. The agency aims to harness the technology for its own operational benefits while simultaneously assessing its implications on public service. Project Galileo, an initiative spearheaded by the GAO, emphasizes the importance of maintaining oversight in AI usage across the federal landscape.
Taka Ariga, the chief data scientist and director of the GAO Innovation Lab, elaborates on this approach:
“The more use cases we develop, the more of a practitioner’s point of view we bring to audits. And on the flip side, the more evaluations we do, the more conscientious we can be with our own use cases.”
This iterative cycle of developing use cases and conducting evaluations reinforces the GAO’s commitment to being an influential watchdog, promoting responsible AI implementation while ensuring that government agencies adhere to best practices and ethical standards.
OPM’s Structured Approach to AI Implementation
The Office of Personnel Management (OPM) is also leaning into generative AI with a clear strategy designed to enhance human resources and operational planning. Guy Cavallo, CIO of OPM, anticipates significant positive impacts on HR capital planning through the use of these emerging technologies. To this end, OPM is establishing a steering committee responsible for vetting potential projects and is actively recruiting AI experts to oversee implementation.
The agency’s approach integrates generative AI in two primary aspects: by employing proprietary data with open-source models, and through partnerships with commercial software that embeds AI functionalities, such as Microsoft Copilot. This phased rollout is indicative of OPM’s careful strategy to adopt technology while ensuring it enhances their operational effectiveness.
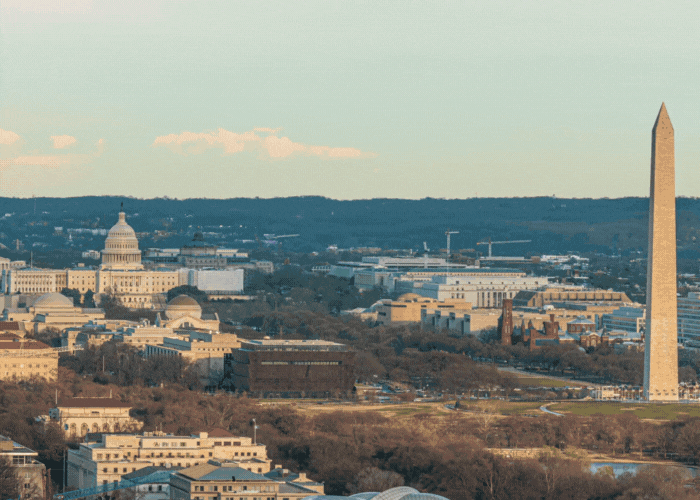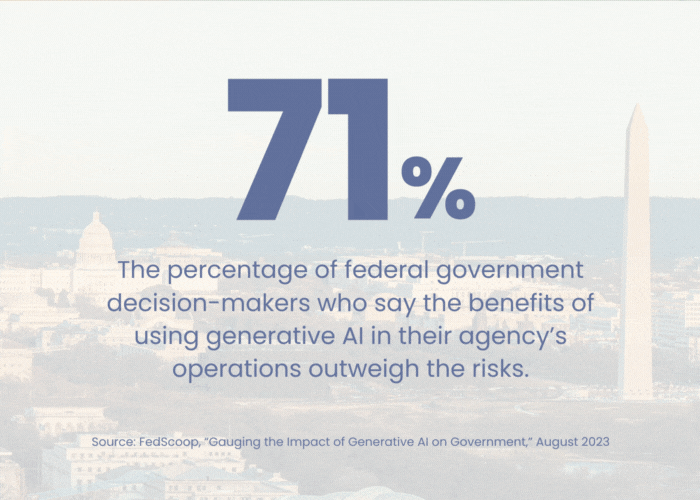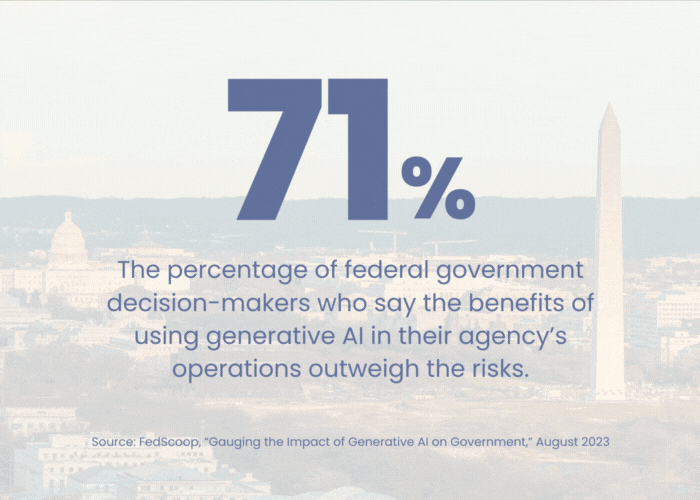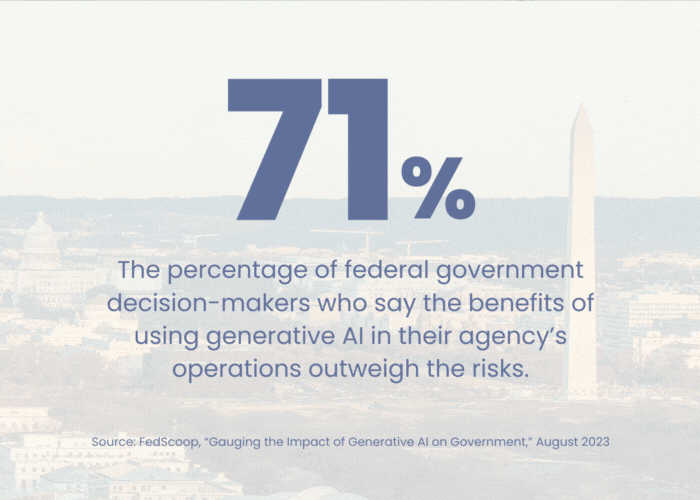 The future of HR operations with AI.
The future of HR operations with AI.
Black Hat Preview: Security Takes Center Stage
As federal agencies explore generative AI, the looming specter of security concerns cannot be overlooked. The Black Hat security conference, often dubbed “Hacker Summer Camp,” serves as a pivotal platform for discussing AI security dynamics within the enterprise landscape. This year, the conference showcases presentations focused on addressing vulnerabilities related to cloud security and large language models (LLMs).
Richard Harang, a principal security architect at NVIDIA, will delve into the critical aspect of LLM security in his talk entitled “Practical LLM Security: Takeaways From a Year in the Trenches.” His insights draw from extensive practical experience securing LLM applications, focusing on the prevalent threats that persist in this evolving technological landscape. NVIDIA has implemented numerous AI-powered solutions across its portfolio, with their AI Red Team playing a central role in identifying and mitigating potential attacks against these systems.
Emerging Threats in Cloud Security
The magnitude of security threats in cloud environments continues to escalate, with enterprises clamoring for effective solutions to safeguard their infrastructures. Black Hat is poised to reveal critical vulnerabilities, such as those uncovered by researchers from Aqua Security, relating to Amazon Web Services (AWS). The findings, which highlight previously undisclosed flaws that could have allowed external attackers to breach almost any AWS account, underscore the urgent need for vigilant security practices and robust defenses in cloud architecture.
Another compelling presentation will come from security researchers at Tenable, who are expected to unveil a significant remote code execution vulnerability affecting millions of cloud servers. Dubbed CloudImposer, this vulnerability emerged from a mere faulty command argument—an unsettling reminder of the delicate nature of security in an interconnected environment.
 Addressing cloud security challenges dynamically.
Addressing cloud security challenges dynamically.
Navigating Cyber Threats: The Need for Proactive Measures
The intersection of generative AI and cybersecurity illuminates the pressing need for agencies to fortify their defenses while embracing innovation. Federal agencies must continue to strike a delicate balance between leveraging the potential of generative AI and safeguarding against the associated risks and vulnerabilities. As representatives from these agencies gather insights from conferences like Black Hat, the dialogue around establishing comprehensive security frameworks becomes increasingly relevant.
As these technologies evolve, it is vital that policymakers, technical experts, and agency leaders collaborate to create robust oversight mechanisms that can continually adapt to the rapidly changing technological landscape. Ensuring that emerging AI systems not only function effectively but do so through responsible and secure channels will be paramount for the future integrity of government operations and public trust.
Conclusion: A New Era of Responsible AI Utilization
In the era of AI, federal agencies are embarking on a transformative journey, exploring generative AI technologies to improve operational efficiency while maintaining ethical considerations. The Air Force, GAO, and OPM demonstrate how federal entities are actively engaging with these technologies, shaping their strategic approach to innovation.
As we progress into this new frontier, the lessons learned in integrating AI solutions—while protecting citizen data—will guide the framework for future innovations. Responsible AI utilization, coupled with unwavering commitment to security, will dictate the success of these initiatives, charting a course for a secure and efficient federal landscape in the years to come.
This exploration of federal agencies’ foray into generative AI underlines an essential narrative: the quest to harness transformative technologies must be met with equal diligence towards oversight and ethics.


 Photo by
Photo by 











