Unveiling the Future: ASUS, AI, and the Race Against Time
The Quiet Rise of ASUS in the Tech Arena
ASUS, a name primarily associated with laptops and Wi-Fi equipment, is making strides to carve out a significant space in the enterprise technology and cloud sector. The recent Computex conference in Taiwan served as a platform for ASUS to showcase its ambitions. During the event, Jackie Hsu, senior vice president and co-head of the Open Platform Business and IoT groups, revealed the company’s burgeoning plans in the cloud and enterprise realms, demonstrating impressive successes domestically that hint at a larger vision for global expansion.
 ASUS at Computex: Innovating for the Future
ASUS at Computex: Innovating for the Future
Building Supercomputers: Taiwania’s Legacy
Hsu highlighted that ASUS played a pivotal role in the development of the Taiwania 2 supercomputer—a powerhouse capable of 9 petaflops, ranking 20th on the Top 500 Supercomputers list upon its debut. This significant achievement cemented ASUS’s initiative in high-performance computing, and the company is now tasked with constructing the Taiwania 4 supercomputer, showcasing its commitment to advancing supercomputing capabilities in Taiwan.
With an exceptional power usage efficiency (PUE) rating of 1.17, the newly built datacenter is designed to handle the immense computational requirements of Taiwania 4. Achieving such efficiency in Taiwan’s hot and humid climate is commendable, marking ASUS as a serious contender in global tech infrastructure.
The Formosa Foundation Model: Advancing Language AI
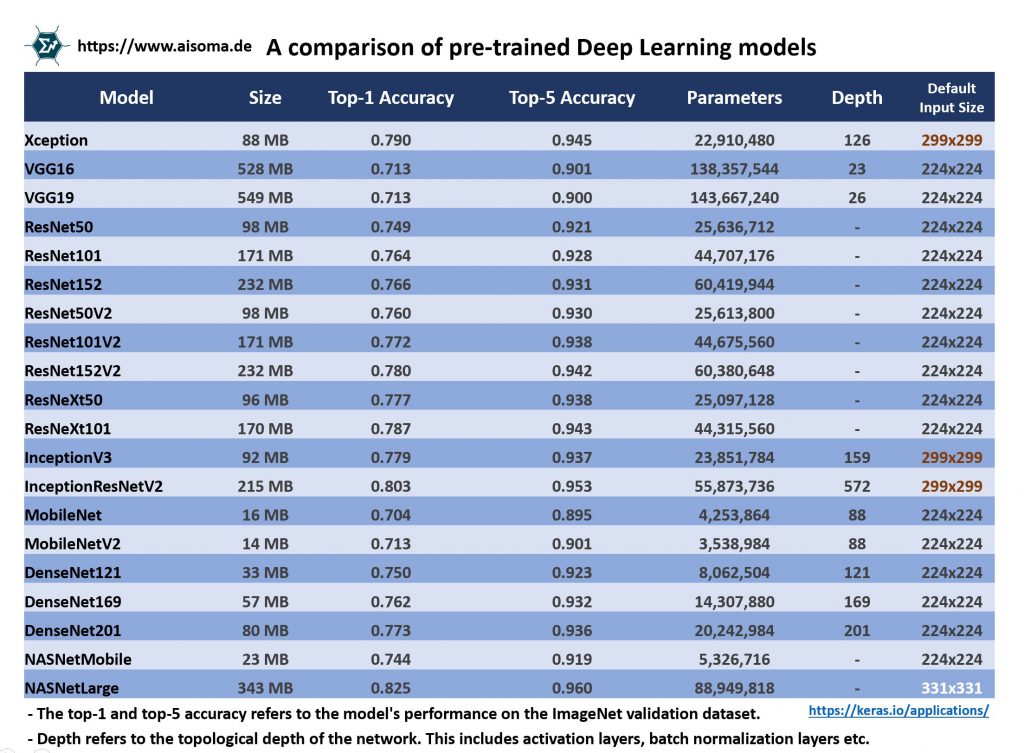
An exciting yet lesser-known initiative from ASUS is the Formosa Foundation Model, a large language model (LLM) characterized by a staggering 176 billion parameters, specifically tuned to handle traditional Chinese semantics. Hsu emphasized the importance of developing LLMs that incorporate local languages, stating that models predominantly trained on American English lead to an underrepresentation of non-English linguistic nuances.
The Formosa Foundation Model positions ASUS uniquely in a landscape where many AI advancements are dominated by Western languages, reiterating the need for diverse language models as AI technology continues to pervade various sectors. The potential applications of such a model in delivering AI solutions tailored for Taiwanese clients are monumental, offering a glimpse into ASUS’s future in AI.
 Comparing AI Models: Global Language Adaptation
Comparing AI Models: Global Language Adaptation
Competing with Giants in Server Technology
Traditionally, ASUS has offered a plethora of server types, from vanilla to specialized AI servers, but has often overlooked the competitive nature of the server market, falling short against more prominent players. However, Hsu noted that ASUS has engaged hyperscalers, presenting itself as a reliable supplier able to showcase energy-efficient server designs. Clients who are unable to match ASUS’s remarkable efficiency in creating datacenters have begun to take notice.
The engagement with clients extends beyond mere server supply; ASUS is crafting substantial systems for AI, effectively providing a comprehensive hardware and software stack. Although the company may not be able to compete on price, as stated by Hsu, it offers sufficient value through its entire solution package, positioning itself as an attractive option in the enterprise landscape.
The Potential for Growth and Transformation
Reflecting on these strategic developments, Hsu expressed optimism, stating, “This is definitely a big growth area for us.” The potential for ASUS to establish a stronger foothold in the enterprise space aligns with the surging demand for computing power, particularly with burgeoning interests in AI. ASUS’s efforts seem timely; as interest in AI solutions increases, so too does the potential for the company to thrive not only in Taiwan but also in international markets.
OpenAI’s Sora: A Double-Edged Sword
The advancements by ASUS occur against a backdrop of rapid developments in the AI space, notably exemplified by OpenAI’s recent unveiling of Sora, a video generator renowned for its cinematic quality. The implications for the entertainment industry are profound, as Sora’s capabilities further rouse the debate surrounding AI training on copyrighted content without consent. While OpenAI touts that Sora is trained on “publicly available” works, the murkiness surrounding its methodologies raises ethical concerns. Reports indicate that at least one million hours of YouTube videos were utilized without payment or agreement from content creators.
 The Future of AI in Hollywood: Opportunities and Challenges
The Future of AI in Hollywood: Opportunities and Challenges
Movies or Misinformation?
This situation highlights a fundamental crisis in the relationship between generative AI, creators, and copyright. Unlike platforms such as Google, which initially showcased snippets from copyrighted texts without directly competing with them, OpenAI’s Sora threatens to directly replace the market value of these creative works. Lalit Yan, a prominent musician, voiced that artists deserve compensation for their creations, urging more responsible practices surrounding AI training.
The controversy encompasses not only ethical considerations but also practical frustrations among creators who find their works plundered for the advancement of AI models. As industry leaders weigh the implications, transparency in data sourcing and offers of consent become increasingly critical.
Legislative Response and the Push for Transparency
Recent initiatives, including President Joe Biden’s Executive Order on AI, aspire to enhance transparency in generative AI practices. Congress has responded with proposals such as The Generative AI Copyright Disclosure Act, which would require AI developers to disclose the nature of datasets used in training, ensuring that rights holders are informed about the usage of their content.
Legislative measures are gaining traction amidst growing public concern over accountability in technology. For instance, leading music artists like Billie Eilish are advocating for stricter rules against the unauthorized use of creative content in training AI models, signaling a shift toward ethical AI practices.
 The Legislative Landscape of AI: Protecting Creators Rights
The Legislative Landscape of AI: Protecting Creators Rights
Conclusion: The Horizon of AI and Its Ethical Challenges
As ASUS expands into enterprise technology and AI, it faces both formidable competition and the pressing need for ethical accountability in AI practices. The company’s visionary projects signal significant transformations for the tech landscape, while ongoing controversies like those surrounding OpenAI’s Sora serve as reminders of the ethical responsibilities that accompany these advancements.
The intersection of technological potential with questions of ethics and copyright will continue to shape the narrative within the AI sector. As companies like ASUS position themselves for success in both local and global markets, their ability to prioritize responsible practices will define their standing not only as innovators but as stewards of the industry’s future.














